GRACE LE
BUILDS IT!
Rolling Vehicles Project
"Sweet Sensation"

What's Going On??
Regina Vermina wants us to help her get the amusement park up and running. She is in need!! Regina wants us to make vehicles that go fast and as straight as possible. But there is a catch, the vehicles must be safe for passengers who ride in them. Can you help her come up with a vehicle that is fun but safe for her amusement park? Right! Let's get to it!!
 A Cereal Box |  1/4" Dowel Rods |
|---|---|
 4 CD's |  4 Wooden Square/Rectangle Adapters |
 4 Foam Square Bearings |  Gummy Worms, Duck Tape, Hot Glue Gun |
What Do I Need For This?
How It Was Built!
Step 1:
Draw and design your car!

Step 2:
Put the pieces together and start assembling them!



Step 3:
Let's put them to the ultimate test!
*Make sure that your gummies stay on real tight!

Now Let's Test It!
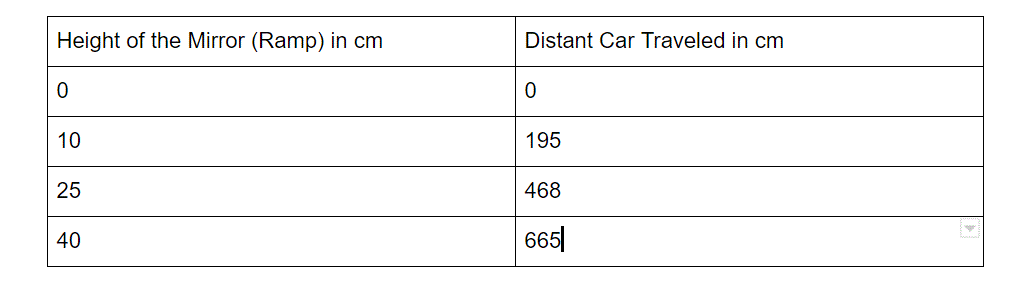
Once you finish your vehicles, it's now the time to test it out! What you will need is to find a ramp for your vehicle to start moving. For this, I used a mirror. After you find a ramp, pick out three heights you want our car to start in. I chose 0cm, 10cm, 25cm, and 40cm. As soon as you measure the height, make sure you set the back two wheels of your car touching the start of your ramp. Once you let go and the car stops, you can measure how far the car went. You may ask, "how do I measure how far the car went?" Well, let me share with you a little secret!



Ramp height: 10cm Ramp height: 25cm Ramp height: 40cm
Total Distance: 322cm
Total Distance: 595cm
Total Distance: 790cm
Crash Test Time! Let's hope they make it!!
Ramp height: 0cm
Total distance: 0cm

How To Measure By...
STEP SIZES!
To measure your steps, you are going to see how many steps you take in a certain length. In my class, we used 30 meters and within 30 meters, it took me 38.5 steps to reach to the end. Since I took about 38.5 steps in 30 meters, so, therefore, I took 78cm for every step. Here are the calculations.
1m=1cm
30m=3000cm
3000
38.5
=78cm/step
How many steps(Size of steps)+length of ramp=total distance
Ramp height: 0cm
Traveled zero distance
Ramp height: 10cm
2.5(78)+127=322cm
Ramp height: 25cm
6(78)+127=595
Ramp height: 40cm
8.5(78)+127=790
Let's Look at the Data:

Why is a Line Graph is Best Option?
A line graph helps show the relationship between the independent variable ( the height of the ramp) and the dependent variable (distance car traveled). It also shows continuous growth!
Independent Variable:
- I can change or manipulate the independent variable. It is represented on the x-axis. Our independent variable is going to be the ramp height because I was able to change it each time.
Dependent Variable:
- The dependent variable is the one that can't be manipulated and is always affected by the independent variable. It is represented on the y-axis. My dependent variable is going to be the distance traveled because I have no control over how long the car travels.
More Resources on Graphing!
Connection to Science!
Gravity:
Due to gravity being placed on an unbalanced force towards the car, it was able to travel down the ramp. However, when I place the ramp at 0 cm "tall," the car won't move or travel anywhere because gravity was unable to pull the car down due to it already being on the ground.
Friction:
Friction causes the car to slow down, and eventually, stop. Bascially when two objects rub against each other, a force is created, aka force. Without friction, the car could travel for awhile because nothing is stopping it.
Energy Transfer:
Energy is something that can never be created, nor destroyed. But how? So the energy comes from the sun. The sun gives light to the plants, which are consumed by humans and other animals. People eat animals, we hold thier engery and place it on the car on the ramp.
Newton's Law and Seatbelts:
Newton's Law states that an object have inertia, so that means an object will continue to move at the same speed in the same direction unless acted on by an unbalanced force. With this law, it says that my gummy worms will continue to travel in a straight line unless an unbalanced force stops it. In this case, the seatbelts acted as an unbalanced force to keep my gummy worms from flying off of the car. If I didn't have the seatbelt then my worms would have fallen and failed the crash test.
More Resources!
K-6 Science Curriculum
1.P.1 Understand how forces (pushes or pulls) affect the motion of an object.
3.P.1 Understand motion and factors that affect motion.
3.P.3 Recognize how energy can be transferred from one object to another.
4.P.1 Explain how various forces affect the motion of an object.
4.P.3 Recognize that energy takes various forms that may be grouped based on their interaction with matter.
5.P.1 Understand force, motion and the relationship between them.
5.P.2 Understand the interactions of matter and energy and the changes that occur.
6.P.3 Understand characteristics of energy transfer and interactions of matter and energy.
Common Core Math Standards
-
Describe and compare measurable attributes.
-
Measure and estimate length in standard units.
-
Represent and Interpret Data.
-
Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes.
-
Generate measurement data by measuring lengths of several objects to the nearest whole unit, or by making repeated measurements of the same object. Show the measurements by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in whole-number units.